本文最后更新于 2024-03-22T23:32:53+00:00
官方源码:https://github.com/facebook/react
预防针:看过 Vue 源码的正常,不看 React 源码的也正常,因为它非常复杂,未必能看懂,所以看懂一部分就行了。
看了 React 源码与写好 React 没啥关系。
这篇文章能带来的是:搞清楚 React 的工作流程,基于 React 的 17 版本源码
引子 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <div><h2 > hello world </h2 > <div > { text }</div > map (item =><ChildItem item ={item} > </ChildItem >
问题:list 数据改变时,怎么最快的判断出来如何更新?一律采用从头(根节点)遍历,然后再跟之前的对比,把有区别的更新下 。
React 为什么要用 Fiber? 因为 React 采用的更新策略是从根节点递归遍历,然后再跟之前的对比,把有区别的更新下
React 大概的版本区别
V15 版本,Stack Reconciler:同步更新机制
16.9 ~ 17.0.2 版本,Fiber Reconciler:异步可中断更新机制
但在 17.0.2 里面只是先做了数据结构,但不稳定(可以理解为先吹了一波),有两个模式
legacy 模式:可通过 createa 脚手架创建,有 Fiber 的结构,但不会中断,源码文件为 xxx.old.js
concurrent 模式:需要自己去编译,无法通过 create 脚手架创建,实现了中断,源码文件为 xxx.new.js
18 版本,可以理解为 concurrent 模式 ++
React 中的数据结构 v-dom / element 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 function App (return <div className ="app" > <h2 > hello world</h2 > <div id ="list" > <ul > <li > list 1</li > <li > list 2</li > <li > list 3</li > </ul > </div > </div > function App (return React .createElement ('div' , { className : 'app' },React .createElement ('h2' , null , 'hello world' ),React .createElement ('div' , { id : 'list' },React .createElement ('ul' , null ,React .createElement ('li' , null , 'list 1' ),React .createElement ('li' , null , 'list 2' ),React .createElement ('li' , null , 'list 3' )
那React.createElement到底是个啥?源码地址:点这个
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 function ReactElement (type , key, ref, self, source, owner, propsconst element = {$$typeof : REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE ,type : type ,key : key,ref : ref,props : props,_owner : owner,return element;export function createElement (type , config, childrenlet propName;const props = {};if (config != null ) {for (propName in config) {if (call (config, propName) &&RESERVED_PROPS .hasOwnProperty (propName)const childrenLength = arguments .length - 2 ;if (childrenLength === 1 ) {children = children;else if (childrenLength > 1 ) {const childArray = Array (childrenLength);for (let i = 0 ; i < childrenLength; i++) {arguments [i + 2 ];if (__DEV__) {if (Object .freeze ) {Object .freeze (childArray);children = childArray;return ReactElement (type ,ReactCurrentOwner .current ,
通过上述的React.createElement源码可得如下结构(vDom):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 function App (return React .createElement ('div' , { className : 'app' },React .createElement ('h2' , null , 'hello world' ),React .createElement ('div' , { id : 'list' },React .createElement ('ul' , null ,React .createElement ('li' , null , 'list 1' ),React .createElement ('li' , null , 'list 2' ),React .createElement ('li' , null , 'list 3' )const vDom = {type : "div" ,props : {className : "app" ,children : [type : "h2" ,props : { children : "hello world" },type : "div" ,props : {id : "list" ,children : [type : "ul" ,props : {children : [type : "li" ,props : { children : "list 1" },type : "li" ,props : { children : "list 2" },type : "li" ,props : { children : "list 3" },
fiber 本质就是一个链表形式的数据结构,用来表示 v-dom 的,大致结构如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 FiberNode = {return ,
current Fiber、workInProgress Fiber current Fiber:对应当前页面中真实渲染的 DOM 的结构
React 的双缓存是什么? 双缓存来源于:图形渲染的优化技术
在双缓存技术中,系统会在内存(通常为显存)中开辟两个区域:
前缓冲(Front Buffer):这是与显示器相连的缓冲区,当前正在被显示的内容就存储在这里。
后缓冲(Back Buffer):这是一个独立于前缓冲的内存区域,应用程序在该区域进行所有的绘图操作。
应用程序会在后缓冲中完成所有的图形绘制工作,而不会直接影响到屏幕上显示的内容。
当所有需要更新的画面内容都在后缓冲区绘制完成后,系统会执行一次“缓冲区交换”或“页面翻转”操作,迅速将前后缓冲区的角色互换,即将后缓冲区的内容复制到前缓冲区,并使其成为新的可见帧。
由于这个交换操作通常是硬件加速且非常快速的,因此用户看到的是一个完整、无闪烁的新帧画面,而不是半成品或者绘制过程中的中间状态。
简单理解为:预加载
React 中的双缓存指的是两个 Fiber 树,一个用于当前展示(current fiber),一个用于更新的(workInprogress fiber),有变化时则创建workInprogress fiber并在其中进行比较、计算等,之后直接一次性用整个workInprogress fiber(或部分) 替换掉整个current fiber(或部分),不用两个逐个比较与 DOM 更新,从而避免了大量的 DOM 操作带来的性能损耗。
React 的核心库
react 库1、提供虚拟 DOM 相关的 API;2、提供用户相关的 API(useState/use* 等)react-dom 库提供操作 DOM 相关的 API
其中的核心库 react-reconciler通过调和、调度、提交等过程实现渲染
其中核心的为:
ReactFiberBeginWork.js:创建 workInProgressFiber
ReactFiberCompleteWork.js:基于 workInProgressFiber 创建 EffectList
ReactFiberCommitWork.js:基于 EffectList 更新界面
React 的整体流程(V17 版本) 页面代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 function App (return <div className ="app" > <h2 > hello world</h2 > <div id ="list" > <ul > <li > list 1</li > <li > list 2</li > <li > list 3</li > </ul > </div > </div > ReactDom .render (<App /> document .getElementById ('root' ));
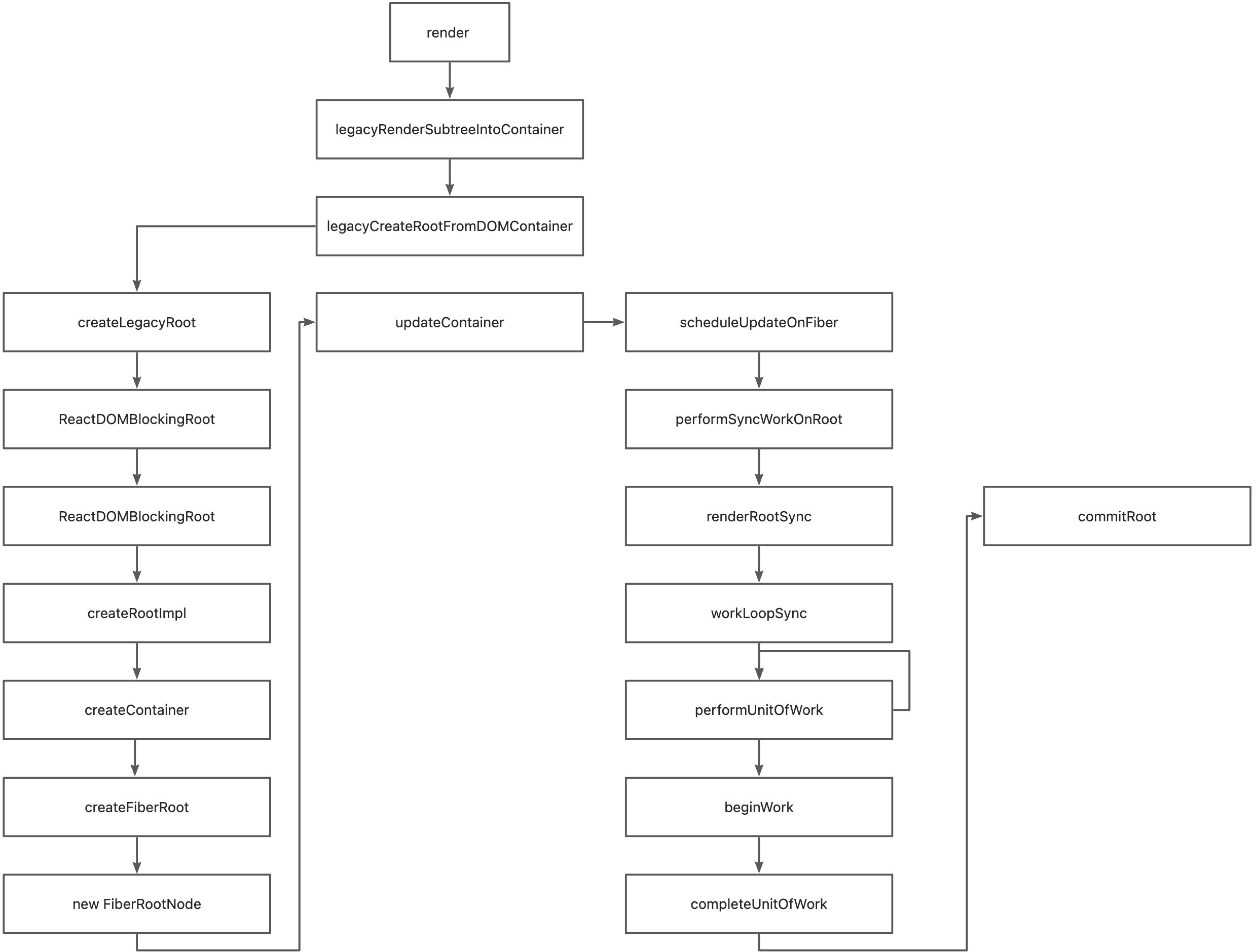
入口:页面的ReactDom.render(...),调用的源码是react-dom 库里面的render函数 源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 export function render ( element: React$Element<any >, container: Container, callback: ?Function , return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer ( null ,false ,
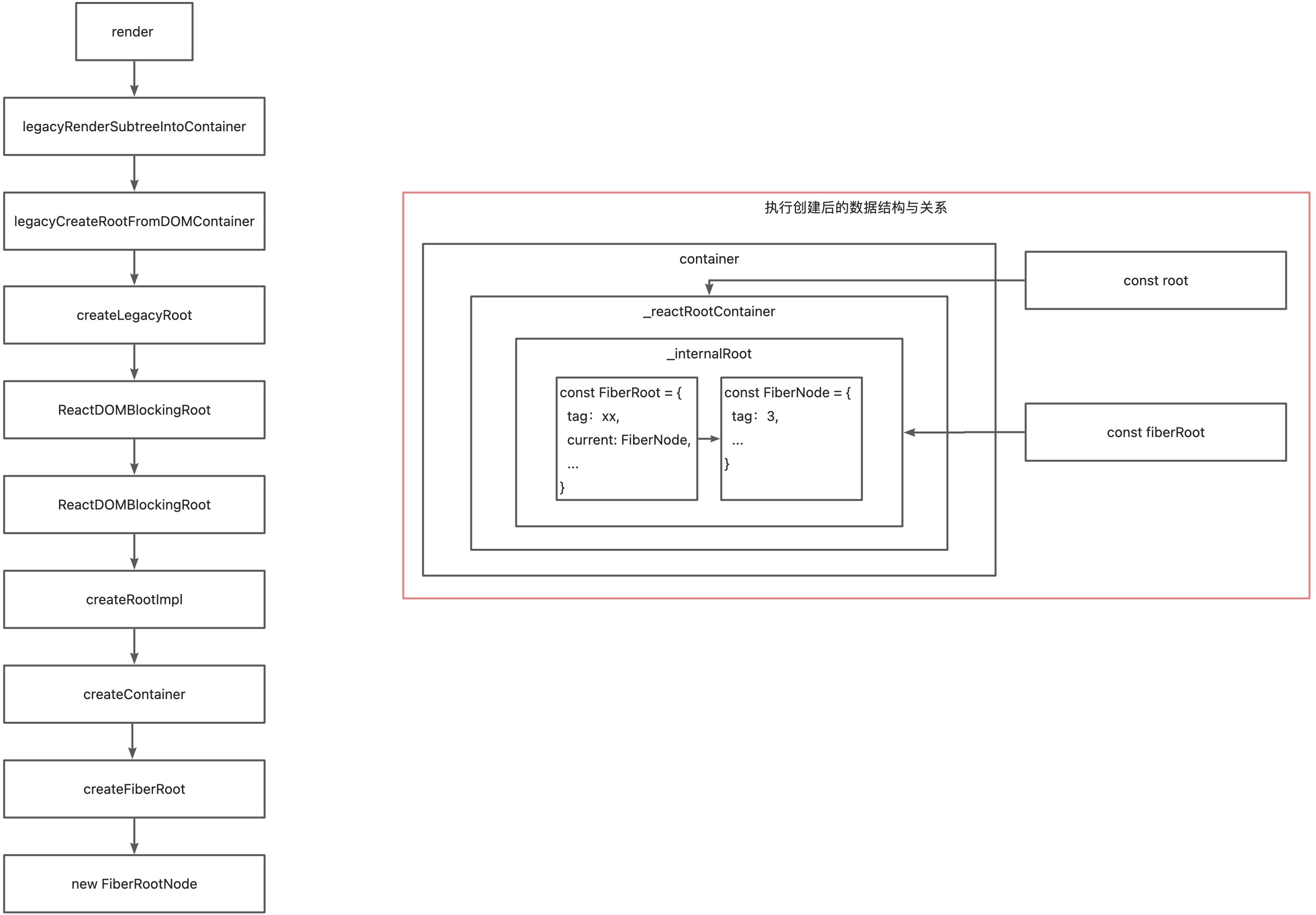
legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer:将子树渲染到容器中,首次渲染则调用legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer ( parentComponent: ?React$Component<any , any >, children: ReactNodeList, container: Container, forceHydrate: boolean , callback: ?Function , React $Component<any , any > | PublicInstance | null {let root : RootType = (container._reactRootContainer : any );let fiberRoot;if (!root) { _reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer (_internalRoot ;unbatchedUpdates (() => {updateContainer (children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);else { _internalRoot ;updateContainer (children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);return getPublicRootInstance (root);
legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer:用于创建 React 的根节点(FiberRoot),核心为createLegacyRoot源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 function legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer ( container: Container, forceHydrate: boolean , RootType {return createLegacyRoot (hydrate : true ,undefined ,
createLegacyRoot:用于创建 React 的根节点(FiberRoot),核心为ReactDOMBlockingRoot源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 export function createLegacyRoot ( container: Container, options?: RootOptions, RootType {return new ReactDOMBlockingRoot (container, LegacyRoot , options);
ReactDOMBlockingRoot:核心调用createRootImpl源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 function ReactDOMBlockingRoot ( container: Container, tag: RootTag, options: void | RootOptions, this ._internalRoot = createRootImpl (container, tag, options);ReactDOMRoot .prototype render = ReactDOMBlockingRoot .prototype render = function (ReactDOMRoot .prototype unmount = ReactDOMBlockingRoot .prototype unmount = function (void { ... }
createRootImpl:核心调用createContainer源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function createRootImpl ( container: Container, tag: RootTag, options: void | RootOptions, const root = createContainer (container, tag, hydrate, hydrationCallbacks);return root;
createContainer:核心调用createFiberRoot源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 export function createContainer ( containerInfo: Container, tag: RootTag, hydrate: boolean , hydrationCallbacks: null | SuspenseHydrationCallbacks, OpaqueRoot {return createFiberRoot (containerInfo, tag, hydrate, hydrationCallbacks);
createFiberRoot:核心调用new FiberRootNode源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 export function createFiberRoot ( containerInfo: any , tag: RootTag, hydrate: boolean , hydrationCallbacks: null | SuspenseHydrationCallbacks, FiberRoot {const root : FiberRoot = (new FiberRootNode (containerInfo, tag, hydrate): any );const rootFiber = createHostRootFiber (tag);current = rootFiber; return root;
FiberRootNode:一个构造函数,生成Fiber Root Node的数据结构源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 function FiberRootNode (containerInfo, tag, hydrate ) {this .tag = tag;this .containerInfo = containerInfo;this .pendingChildren = null ;this .current = null ;this .pingCache = null ;this .finishedWork = null ;this .timeoutHandle = noTimeout;this .context = null ;this .pendingContext = null ;this .hydrate = hydrate;this .callbackNode = null ;this .callbackPriority = NoLanePriority ;this .eventTimes = createLaneMap (NoLanes );this .expirationTimes = createLaneMap (NoTimestamp );this .pendingLanes = NoLanes ;this .suspendedLanes = NoLanes ;this .pingedLanes = NoLanes ;this .expiredLanes = NoLanes ;this .mutableReadLanes = NoLanes ;this .finishedLanes = NoLanes ;this .entangledLanes = NoLanes ;this .entanglements = createLaneMap (NoLanes );if (supportsHydration) {this .mutableSourceEagerHydrationData = null ;if (enableSchedulerTracing) {this .interactionThreadID = unstable_getThreadID ();this .memoizedInteractions = new Set ();this .pendingInteractionMap = new Map ();if (enableSuspenseCallback) {this .hydrationCallbacks = null ;
总结一下前面创建Fiber Root的流程
创建之后,后续关键调用为updateContainer,其中关键为scheduleUpdateOnFiber 源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 export function updateContainer ( element: ReactNodeList, container: OpaqueRoot, parentComponent: ?React$Component<any , any >, callback: ?Function , Lane {const current = container.current ;const update = createUpdate (eventTime, lane);scheduleUpdateOnFiber (current, lane, eventTime);return lane;
源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber ( fiber: Fiber, lane: Lane, eventTime: number , const root = markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot (fiber, lane);if (lane === SyncLane ) {performSyncWorkOnRoot (root);else {ensureRootIsScheduled (root, eventTime);schedulePendingInteractions (root, lane);if (executionContext === NoContext ) {resetRenderTimer ();flushSyncCallbackQueue ();else {if (DiscreteEventContext ) !== NoContext &&UserBlockingSchedulerPriority ||ImmediateSchedulerPriority )if (rootsWithPendingDiscreteUpdates === null ) {new Set ([root]);else {add (root);ensureRootIsScheduled (root, eventTime);schedulePendingInteractions (root, lane);
源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 function performSyncWorkOnRoot (root ) {renderRootSync (root, lanes);commitRoot (root);return null ;
renderRootSync:关键调用workLoopSync源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 function renderRootSync (root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes ) {workLoopSync ();return workInProgressRootExitStatus;
源码位置:点这
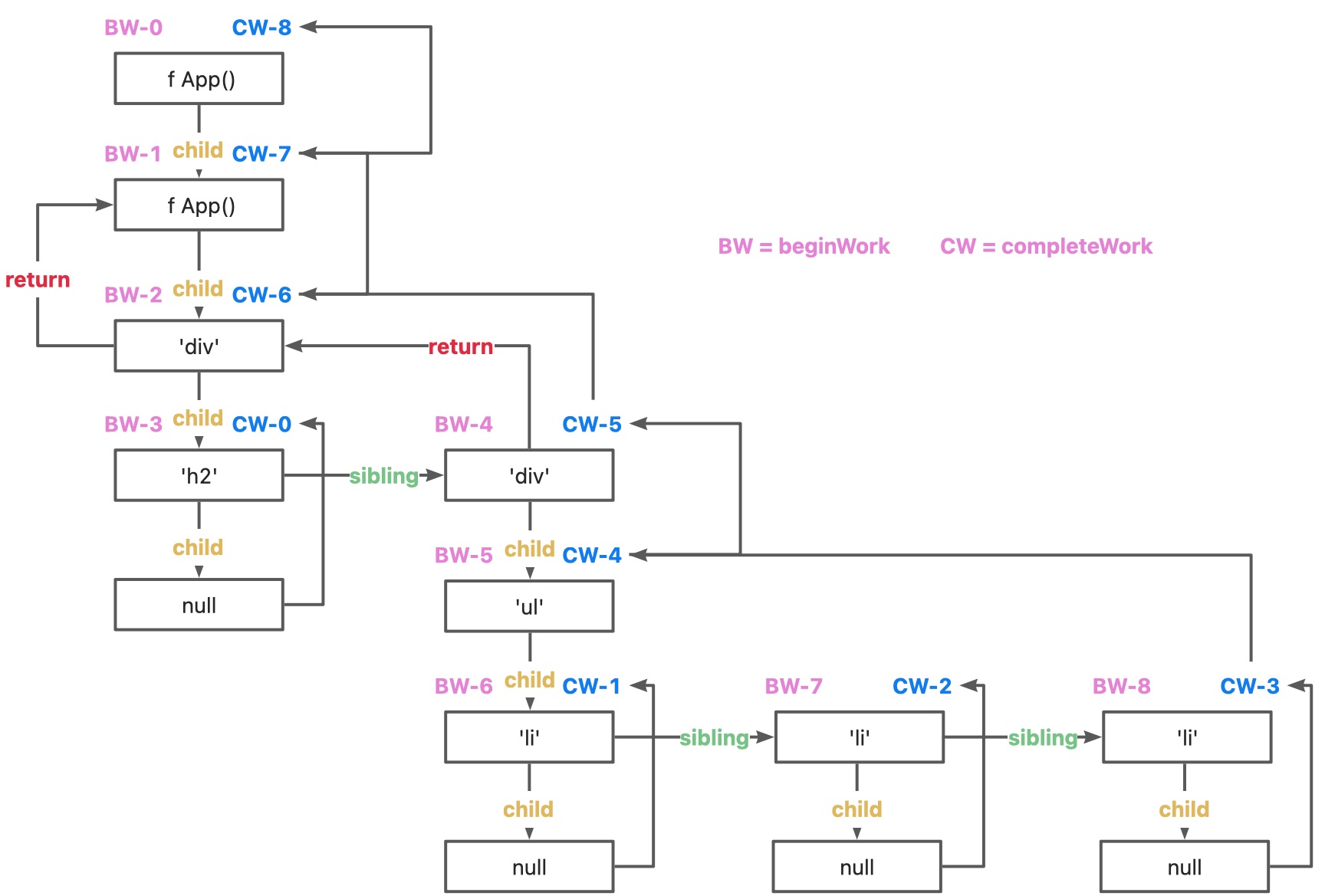
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 function workLoopSync (while (workInProgress !== null ) {performUnitOfWork (workInProgress);function App (return <div className ="app" > <h2 > hello world</h2 > <div id ="list" > <ul > <li > list 1</li > <li > list 2</li > <li > list 3</li > </ul > </div > </div > ReactDom .render (<App /> document .getElementById ('root' ));3 ,elementType = null ,代表 container2 ,elementType = f App (),代表 function App (5 ,elementType = 'div' ,代表 <div className="app" > 元素5 ,elementType = 'h2' ,代表 <h2> 元素5 ,elementType = 'div' ,代表 <div id="list" > 元素5 ,elementType = 'li' ,代表 <li>list 3 </li> 元素
源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 function performUnitOfWork (unitOfWork: Fiber ): void {let next;beginWork (current, unitOfWork, subtreeRenderLanes);if (next === null ) {completeUnitOfWork (unitOfWork);else {ReactCurrentOwner .current = null ;
所以递归逻辑为:先子级后同级(先深度后广度)workLoopSync递归调用performUnitOfWork处理同级,performUnitOfWork调用beginWork处理子级
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function App (return <div className ="app" > <h2 > hello world</h2 > <div id ="list" > <ul > <li > list 1</li > <li > list 2</li > <li > list 3</li > </ul > </div > </div >
递归调用逻辑图(Fiber 链表结构) Fiber的数据结构,核心就是:return(父)、child(子)、sibling(兄)
beginWork:作用是创建 workInProgressFiber源码位置:点这 v-dom,然后和current fiber对比,向下调和的过程effectTag
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 function beginWork ( current: Fiber | null , workInProgress: Fiber, renderLanes: Lanes, Fiber | null {const updateLanes = workInProgress.lanes ;if (current !== null ) {const oldProps = current.memoizedProps ;const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps ;switch (workInProgress.tag ) {case IndeterminateComponent : {return mountIndeterminateComponent (type ,case LazyComponent : {const elementType = workInProgress.elementType ;return mountLazyComponent (
completeUnitOfWork:核心调用completeWork源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 function completeUnitOfWork (unitOfWork: Fiber ): void {let completedWork = unitOfWork;do {const current = completedWork.alternate ;const returnFiber = completedWork.return ;if ((completedWork.flags & Incomplete ) === NoFlags ) {completeWork (current, completedWork, subtreeRenderLanes);else {
completeWork:核心调用createInstance源码位置:点这 effectList将需要更新的数据形成一个新的 Fiber 链表结构,这样就只需要去更新这些
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 function completeWork ( current: Fiber | null , workInProgress: Fiber, renderLanes: Lanes, Fiber | null {const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps ;switch (workInProgress.tag ) {case IndeterminateComponent :case LazyComponent :case SimpleMemoComponent :case FunctionComponent :case ForwardRef :case Fragment :case Mode :case ContextConsumer :case HostComponent : {const instance = createInstance (type ,invariant (false ,'Unknown unit of work tag (%s). This error is likely caused by a bug in ' +'React. Please file an issue.' ,tag ,
createInstance:核心调用createElement源码位置:点这 @react-dom 库里面的 createInstance创建真实的 DOM(document.createElement()),但还不会渲染到页面上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 export function createInstance ( type : string , props: Props, rootContainerInstance: Container, hostContext: HostContext, internalInstanceHandle: Object , Instance {let parentNamespace : string ;const domElement : Instance = createElement (type ,precacheFiberNode (internalInstanceHandle, domElement);updateFiberProps (domElement, props);return domElement;
createElement:核心调用document.createElement源码位置:点这
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 export function createElement ( type : string , props: Object , rootContainerElement: Element | Document, parentNamespace: string , Element {const ownerDocument : Document = getOwnerDocumentFromRootContainer (let domElement : Element ;if (namespaceURI === HTML_NAMESPACE ) {if (type === 'script' ) {const div = ownerDocument.createElement ('div' );innerHTML = '<script><' + '/script>' ; const firstChild = ((div.firstChild : any ): HTMLScriptElement );removeChild (firstChild);else if (typeof props.is === 'string' ) {createElement (type , {is : props.is });else {createElement (type );if (type === 'select' ) {const node = ((domElement : any ): HTMLSelectElement );if (props.multiple ) {multiple = true ;else if (props.size ) {size = props.size ;else {createElementNS (namespaceURI, type );return domElement;
再总结一下前面的调用栈流程
commitRoot源码位置:点这 beginWork、completeWork完成后,后续关键流程为commitWork,核心调用方法commitRoot,它其中核心调用commitRootImpl
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 function commitRoot (root ) {const renderPriorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel ();runWithPriority (ImmediateSchedulerPriority ,bind (null , root, renderPriorityLevel),return null ;
commitRootImpl源码位置:点这 flushPassiveEffects、commitBeforeMutationEffects、commitMutationEffects、commitLayoutEffects
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 function commitRootImpl (root, renderPriorityLevel ) {do {flushPassiveEffects ();while (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null );commitBeforeMutationEffects (finishedWork);commitMutationEffects (finishedWork, root, renderPriorityLevel);if (shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur) {afterActiveInstanceBlur ();resetAfterCommit (root.containerInfo );current = finishedWork; commitLayoutEffects (root);return null ;
flushPassiveEffects 处理一些还未执行完毕的 useEffect
commitBeforeMutationEffects(更新前) 调用getSnapshotBeforeUpdate生命周期
commitMutationEffects(更新时) 通过 Fiber 链表结构,一层层进行处理增删改
commitLayoutEffects(更新后) 进行 Layout(布局)阶段,执行一些生命周期:componentDidMount、componentWillUpdate 等、执行 setState 的 callback、调用 useLayoutEffect、将 useEffect 存储起来
React 的异步可中断(V18 版本) 中断的是下一次的 beginWork
1 2 3 4 5 6 function workLoopConcurrent (while (workInProgress !== null && !shouldYield ()) {performUnitOfWork (workInProgress);
shouldYield意思是交出执行权。
浏览器的任务执行顺序:宏任务 -> 微任务 -> RAF(requestAnimationFrame) -> render -> RIC(requestIdelCallback) -> 新的 宏任务 -> 新的 微任务 -> …
当面对长任务时,React 会采用分段执行,但又需要满足可打断,先执行后面的,那可以使用的方案如下:
setTimeout:宏任务,满足 render 后再执行,但它存在 4ms 的延迟
Promise:微任务,不满足 render 后再执行,宏任务执行后就立马执行了
requestIdelCallback:在浏览器空闲时期执行,满足 render 后再执行,但它执行时间不确定,兼容性差
MessageChannel:浏览器创建的低延迟通信,可以创建一个宏观上的异步操作,与 render 执行无关
仿照 React 源码,模拟实现打断 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 const queue = []const transition = []let deadTime;const split = 5 const now = (now () const peek = arr => arr[0 ] const poseMessage = (()= >{const { port1, port2 } = new MessageChannel ()ommessgae = () => {peek (transition)()return () => {postMessage () function startTransition (flush ) {push (flush) && poseMessage ()function shouldYield (return now () >= deadTimescheduling .isInputPending function flush (now () + splitconst task = peek (queue) while (task && !shouldYield ()) {const { task } = tasktask = null const next = task ()if (next && typeof next === 'function' ) {task = next else {shift ()startTransition (flush)function schedule (task ) {push ( { task } ) startTransition (flush)function myTask (return () => {console .log (1 )return () => {console .log (2 )return () => {console .log (3 )return () => {console .log (4 )
高优先级操作
Suspense 组件 本质是一个错误边界
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 const fetchList = (return new Promise ((resolve ) => {setTimeout (() => {resolve (["a" , "b" , "c" , "d" ]);1000 );const readApi = (fn ) => {let state = "pending" ;let res;const suspense = fn ()then ((r ) => {"success" ;catch ((err ) => {"error" ;function read (if (state === "pending" ) {throw suspense;else if (state === "error" ) {throw res;else if (state === "success" ) {return res;return read;const ListApi = readApi (fetchList);const List = (const list = ListApi ();return (<div > <ul > {list.map((item) => ( <li key ={item} > {item}</li > ))} </ul > </div > export default function FuncComName (props ) {return (<div > <Suspense fallback ={ <div > loading...</div > }> <List /> </Suspense > </div >
简易手写 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class MySuspense extends Component {constructor (props ) {super (props);this .state = {loading : false ,componentDidCatch (error ) {if (typeof error.then === "function" ) {this .setState ({ loading : true });then (() => this .setState ({ loading : false }));render (return this .state .loading ? this .props .fallback : this .props .children ;
补充 SetTimeout 存在 4ms 的延迟问题
MessageChannel 是浏览器提供的一个高级通信机制,它允许在不同上下文之间(比如窗口、iframe 或者 worker 线程)进行安全且异步的消息传递。
适用于在两个窗口之间建立直接的通信通道。
创建 MessageChannel
1 2 3 4 const messageChannel = new MessageChannel ();const port1 = messageChannel.port1 ;const port2 = messageChannel.port2 ;
发送、接受信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 onmessage = (event ) => {console .log ('收到的信息:' , event.data )postMessage ('喂喂,收得到吗?' )
BroadcastChannel 在相同源的不同上下文之间(包括但不限于标签页)实现双向、异步通信
适用于同一浏览器下的不同窗口进行广播式的通信。
创建 BroadcastChannel
1 2 const channel = new BroadcastChannel ("my_channel" );
发送、接受信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 onmessage = (event ) => {console .log ('收到的信息:' , event.data )postMessage ('喂喂,收得到吗?' )
面试题 什么是 Fiber? 本质是一个对象形式的数据结构:其中包含了虚拟 DOM、链表、EffectList 等数据
创建 fiberRoot 对象,将所有的 dom 串起来
在通过 beginWork 的递归调用,创建出 workInProgressFiber,并打上 EffectTag
然后在 completeWork 中,生成 EffectList,并创建真实的 DOM,在更新前执行一些生命周期,在更新时实现双缓存的切换,在更新后执行一些生命周期
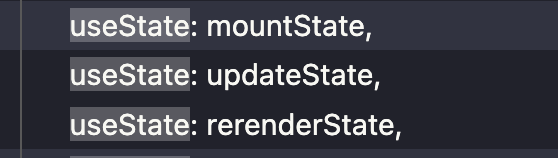
useState 实现原理? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 export function useState<S>(initialState : (() => S) | S,Dispatch <BasicStateAction <S>>] {const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher ();return dispatcher.useState (initialState);function resolveDispatcher (const dispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher .current ;invariant (null ,'Invalid hook call. Hooks can only be called inside of the body of a function component. This could happen for' +' one of the following reasons:\n' +'1. You might have mismatching versions of React and the renderer (such as React DOM)\n' +'2. You might be breaking the Rules of Hooks\n' +'3. You might have more than one copy of React in the same app\n' +'See https://reactjs.org/link/invalid-hook-call for tips about how to debug and fix this problem.' ,return dispatcher;import type {Dispatcher } from 'react-reconciler/src/ReactInternalTypes' ;const ReactCurrentDispatcher = {current : (null : null | Dispatcher ),export default ReactCurrentDispatcher ;export type Dispatcher = {|context : ReactContext <T>,observedBits : void | number | boolean,initialState : (() => S) | S): [S, Dispatch <BasicStateAction <S>>],
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 function mountState<S>(initialState : (() => S) | S,Dispatch <BasicStateAction <S>>] {const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook ();if (typeof initialState === 'function' ) {initialState ();memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;const queue = (hook.queue = {pending : null ,dispatch : null ,lastRenderedReducer : basicStateReducer,lastRenderedState : (initialState : any),const dispatch = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind (null ,return [hook.memoizedState , dispatch]; function basicStateReducer (state, action ) {return typeof action === 'function' ? action (state) : action;function dispatchAction<S, A>(fiber : Fiber ,queue : UpdateQueue <S, A>,action : A,const eventTime = requestEventTime ();const lane = requestUpdateLane (fiber);const update : Update <S, A> = {eagerReducer : null ,eagerState : null ,next : (null : any),const pending = queue.pending ;if (pending === null ) {next = update;else {next = pending.next ;next = update;pending = update;const alternate = fiber.alternate ;if (null && alternate === currentlyRenderingFiber)true ;else {if (lanes === NoLanes &&null || alternate.lanes === NoLanes )const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer ;if (lastRenderedReducer !== null ) {let prevDispatcher;try {const currentState : S = (queue.lastRenderedState : any);const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer (currentState, action);scheduleUpdateOnFiber (fiber, lane, eventTime);
简单理解:但调用 useState 时,会传入一个初始值,useState 会返回一个数组,数组的第一个元素是当前 state 的值,第二个元素是一个 dispatch 方法,并且会记录当前该 hook 对应当前的节点信息(Fiber);若初始值为函数时,还会执行一下获得函数的返回值。
当调用 setState 即 dispatch 方法时,会去触发对应的 Queue.dispatch,本质是执行 setState 传入的内容,然后调用 scheduleUpdateOnFiber 去触发更新逻辑
为什么要使用 useState? 因为 react 的数据本身是不支持响应式的,因为最开始 react 关注的是数据、视图,但后来发现缺少了数据状态的管理,所以也出现了第三方的 Redux 等库来处理。
最后官方意识到了,所以提供了 hooks 的形式,调用它来主动更新页面